What are the symptoms of warts?
Warts are growths on the skin caused by human papillomavirus (HPV) infection. Symptoms can vary depending on the type and location of the wart, but common signs include:
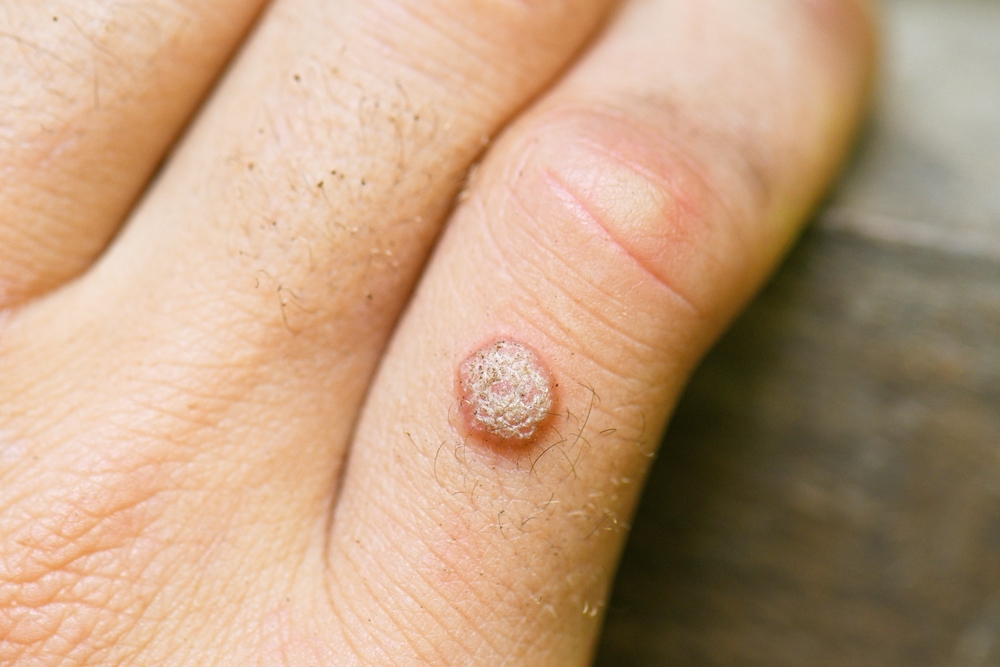
- Small, rough bumps: These are often the first noticeable symptom, with a surface that can be rough or warty.
- Skin color changes: Warts can be flesh-colored, white, or slightly darker than the surrounding skin.
- Pain or tenderness: Some warts, especially those on the feet (plantar warts), can cause pain or discomfort when pressure is applied.
- Bleeding or irritation: Warts can bleed if they are scratched or irritated, and they may be prone to bleeding if they are located in areas where they are frequently bumped or scratched.
- Presence of black dots: Plantar warts may have small black dots in the center, which are tiny, clotted blood vessels.
Warts are usually harmless and can be asymptomatic, but they may cause cosmetic concerns or discomfort depending on their location.
What are the causes of warts?
Warts are caused by an infection with human papillomavirus (HPV). The virus affects the top layer of skin, causing the skin cells to grow rapidly and form warts. Key factors contributing to the development of warts include:
- HPV Infection: The primary cause is infection with specific strains of HPV. Different strains cause different types of warts.
- Direct Skin-to-Skin Contact: Warts can spread through direct contact with an infected person, especially in places like pools or locker rooms.
- Broken Skin: HPV can enter the skin through small cuts, scratches, or breaks, increasing the risk of developing warts.
- Weakened Immune System: A weakened immune system may make a person more susceptible to HPV infections and warts.
- Genetics: Some people may be genetically predisposed to developing warts, as the virus can affect individuals differently based on their immune response and skin characteristics.
Warts are typically benign and can vary in appearance and location, including common warts, plantar warts, flat warts, and genital warts, depending on the HPV strain involved and the area of infection.
What is the treatment for warts?
Treatments for warts aim to remove the wart and eliminate the underlying HPV infection. Various methods can be used depending on the type, location, and number of warts. Common treatments include:
- Over-the-Counter Treatments: Products containing salicylic acid or cryotherapy agents (such as liquid nitrogen) can be applied directly to the wart. These treatments work by peeling off the wart gradually or freezing it off.
- Cryotherapy: This procedure involves applying liquid nitrogen to freeze and destroy the wart. It is typically performed by a healthcare provider.
- Electrosurgery: An electric current is used to burn off the wart tissue. This method can be effective for larger or more stubborn warts.
- Laser Therapy: A laser is used to burn and destroy the wart tissue. This is often used for warts that do not respond to other treatments.
- Chemical Peels: Stronger acids, such as trichloroacetic acid (TCA), can be applied by a healthcare provider to remove warts, especially for genital warts.
- Immunotherapy: This treatment boosts the body’s immune response to fight off the HPV infection. Options include topical medications like imiquimod or interferon injections.
- Minor Surgery: Surgical removal of warts may be necessary for larger or persistent warts. This can be done under local anesthesia.
- Home Remedies: Some people use natural remedies like duct tape occlusion therapy or apple cider vinegar, though these methods lack robust scientific support.
It is essential to consult with a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment, especially if the warts are painful, recurrent, or in sensitive areas like the genital region.
Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.