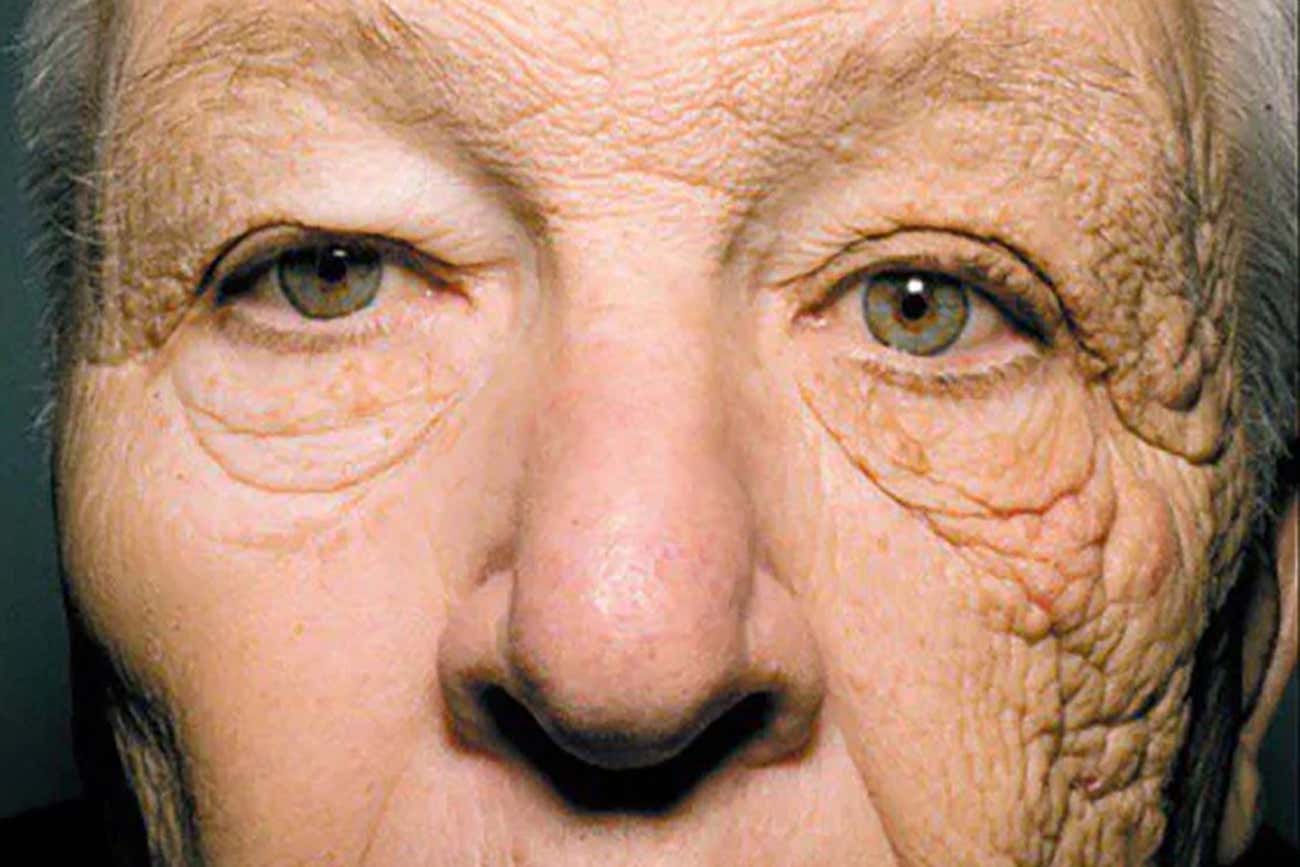
What are the symptoms of wrinkles?
Wrinkles are signs of aging that typically manifest as:
- Fine Lines: Small, shallow lines that often appear around the eyes (crow’s feet), mouth, and forehead.
- Deep Wrinkles: More pronounced and deeper lines that develop over time, commonly seen on the forehead, between the eyebrows (frown lines), and around the mouth (laugh lines or nasolabial folds).
- Loss of Skin Elasticity: The skin may sag or become less firm, contributing to the appearance of wrinkles.
- Dry or Rough Texture: Skin may feel dry, rough, or less smooth as wrinkles develop.
- Creases: Visible folds or creases, often more noticeable when the skin is stretched or relaxed.
Wrinkles can vary in severity and location depending on factors such as age, sun exposure, and lifestyle.
What are the causes of wrinkles?
Wrinkles are caused by a combination of factors, including:
- Aging: As we age, skin loses collagen and elastin, essential proteins that maintain skin’s elasticity and firmness. This leads to the development of wrinkles.
- Sun Exposure: Ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun damages collagen and elastin fibers in the skin, accelerating the formation of wrinkles.
- Genetics: Family history can influence the likelihood and timing of wrinkle development. Some people may be genetically predisposed to developing wrinkles earlier.
- Repeated Facial Movements: Frequent facial expressions, such as smiling, frowning, or squinting, can lead to wrinkles, especially in areas where the skin moves a lot.
- Smoking: Tobacco smoke contains toxins that damage collagen and elastin, leading to premature aging and wrinkles. So quit smoking.
- Environmental Factors: Pollution and harsh weather conditions can contribute to skin damage and wrinkle formation.
- Dehydration: Lack of moisture can make the skin dry and more prone to wrinkling.
- Poor Diet: A diet low in essential nutrients can affect skin health and contribute to wrinkle development.
- Sleep Position: Sleeping in certain positions, such as face-down, can contribute to the formation of sleep lines or wrinkles.
- Health Conditions: Certain health conditions and medications may affect skin elasticity and contribute to wrinkle formation.
A combination of these factors often contributes to the appearance and severity of wrinkles.
What is the treatment for wrinkles?
The treatment for wrinkles can vary based on their severity and the individual’s preferences. Here are some common approaches:
- Topical Treatments:
- Retinoids: Prescription and over-the-counter retinoids, such as tretinoin, can promote cell turnover and stimulate collagen production.
- Moisturizers: Products with ingredients like hyaluronic acid, glycerin, and ceramides help hydrate and plump the skin.
- Antioxidants: Serums containing vitamins C and E can protect the skin from oxidative damage and improve skin texture.
- Procedural Treatments:
- Chemical Peels: These treatments use acids to exfoliate the outer layer of skin, revealing smoother skin underneath.
- Microdermabrasion: A procedure that exfoliates the skin using tiny crystals to remove dead skin cells and improve texture.
- Laser Resurfacing: Lasers can stimulate collagen production and improve skin texture by targeting the deeper layers of the skin.
- Microneedling: This technique involves using fine needles to create tiny punctures in the skin, stimulating collagen production and improving texture.
- Fillers: Dermal fillers, such as hyaluronic acid injections, can temporarily plump up areas with wrinkles and restore volume.
- Botox: Injections of botulinum toxin can relax muscles responsible for dynamic wrinkles, reducing their appearance.
- Lifestyle and Home Remedies:
- Sun Protection: Regular use of sunscreen can prevent further skin damage and reduce wrinkle formation.
- Healthy Diet: Eating a diet rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and healthy fats can support skin health and reduce wrinkle development.
- Hydration: Drinking plenty of water helps maintain skin moisture and elasticity and prevents dehydration.
- Smoking Cessation: Avoiding smoking can help prevent further damage and improve skin appearance.
- Adequate Sleep: Proper sleep can support overall skin health and repair.
- Cosmetic Surgery:
- Facelift: A surgical procedure that removes excess skin and tightens underlying tissues to reduce wrinkles and sagging.
The choice of treatment depends on factors such as the individual’s skin type, the severity of wrinkles, and personal preferences. Consulting with a dermatologist or skincare professional can help determine the most appropriate approach.
Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.